3DS Max PART 00: INTRODUCTION
Hi there!
So, today we’ll make a realistic chair in 3ds max, and then (In next tutorials), make a realistic render by Mental Ray/IRay.
What we need:
- Average knowledge of 3DS max, at least – the creation of simple and extended primitives, edit poly, modifiers.
- Chair photo by http://cmexota.ru/uploads/2010/05/25/brunetka_na_stule09.jpg (there also some other views here: http://cmexota.ru/index.php?newsid=6185). Its simple object, but it’s very good to understand the basics of proper modeling.
In our company, working with 3D graphics, we always adhere to our 3D standard (named “3D_STD”, or simply “Standard”).
Using this standard, we can develop projects faster by using work of various specialists, and not wasting time on compatibility. For non-team users, the standard is good because it can prevent errors and trouble spots in work. I recommend using this standard for everyone.
Unfortunately, this standard is not available in English, but I will translate it and publish on the Internet, as soon, as I can. However, this work will fully comply with it, which I will report on progress.
Because we do not have drawings of this chair, we will use the approximate dimensions of our chair. Overall height is 950 mm, (chair is quite high). The upper point of the seat height is 500 mm. The width of the chair will be equal to 560 mm and length 540 mm chairs will be equal.
PART 01: PREPARE
So, let’s start. Open Autodesk 3ds Max 2012, and check the units, they must be set as mm.
Standard, paragraph 1: Units - only millimeters. Always. Everywhere.
Millimeters to put in two places: In the Units Setup [Main Menu -> Customize -> Units Setup] and in the System Units Setup [Main Menu -> Customize -> Units Setup -> System Units Setup].
In Units Setup we must choose an option “Metric” and choose an item “Millimeters”, like th at:
at:
In System Unit Setup we must choose an item “Millimeters”, like that:
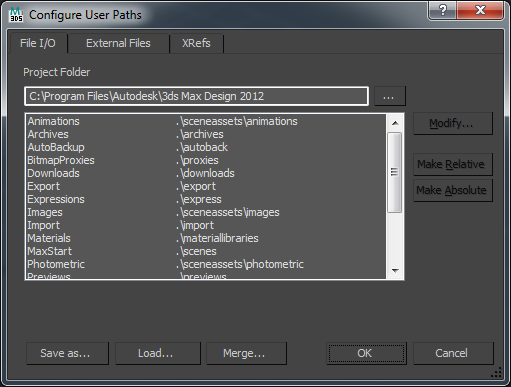
Okay, now let’s set the User Path of 3ds max. Open Configure User Paths [Main Menu -> Customize -> Configure User Paths].
By default, max set the Project Folder at
“C:\Users\UserName\Documents\3dsMaxDesign”.
But in the first versions of 3ds max, this option was a folder, where 3ds max been installed. I do not understand why the Project Folder torn from the folder with the program, but we’ll change it. Push browse button near text block, and set right folder, like that:
“C:\Program Files\Autodesk\3ds Max Design 2012@”
Okay, now you can see that:
Well, now we can start to modeling.
PART 02: MODELING
First, create a bounding box, the size of our chair. Create the container so, that his default pivot point was at 0,0,0.
Box size is 950 mm height, 560 mm width and 540 mm length.
Now, increase the size of the grid. To do this, open the menu Grid and Snap settings [Right-clicking on a magnet with the number three (Snaps Toggle)], and select Home Grid tab. Set 50 mm in Grid Spacing, 10 in Major Lines and 20 in Perspective View Grid Extend:
Okay, close that, and convert our Box to edit poly:
Now we have Edit Poly object which we can change at will. For our task, let’s add additional edges, at 500 mm on Z, which will denote the boundary chair seat.
Select the vertical edges, in Control Panel, scroll to the Edit Edges, and click on the small button to the right of the button Connect (This button allows you to configure the Connect function).
Connect – one of the most popular features in the Edit Poly. It allows you to connect the two edges. In the Connect Settings panel, set value of a Segment = 1, Pinch = 0 and Slide = 0.
After that, our box to be divided into two parts:
Press OK button (Green check).
Now, our edges are at a height of 475 mm, it is necessary to move a little higher, at 500 mm. To do this, press the button W (hotkey to move), and write in the coordinate panel, where been Z label, the height of 500 mm:
So this is our overall container for the chair.
Now make a chair. For a start make the front foot, for this, calculated its estimated diameter, based on the pictures.
Our diameter is 34 mm. Nice.
Someone may say that the easiest way to make foot from an object Capsule, Extended Primitives. But we’ll do it from the spline and turbo smooth.
Using this method, though more complicated, but gives an idea of the right object modeling.
Well, let’s create circle, with radius = 17. Also, set Steps parameter = 1.
Let’s convert this to edit poly. After that, select border in edit poly (Hotkey 3), and select our circle.
Now look at the stunning feature extraction of edge and border. Press and hold shift and move the blue arrow up on the axis Z. As a result, we get a cylinder:
So, move top border to 500 (At the top of chair). Now (Upper boarder must be select), use the command Cap, scroll Edit Borders. Thus we are closing the upper hole.
And now, apply TurboSmooth modifier, with 3 iterations:
Now we have a good preparation for a leg. Remove turbosmooth visible lamp, and apply Connect to the vertical edges. Set the number of segments = 4.
Now, we can turn the lamp in turbosmooth, and observe how the change affected the final segments of the model.
To finish the leg, we must to place our section in the right places. At the bottom of the legs have to be more flat, so the first section is placed at a height of 2 mm, and the second at a height of 10 mm. Second sections we need to “fix” turbosmooth. The fourth section we set at a height of 473 mm, and the fourth at a height of 475 mm.
Okay, result is:
Now, some work with standard:
Standard, paragraph 3: The grid object is always black. The grid light is always yellow by default. The grid cameras are always blue by default.
Standard, paragraph 6: There is a strict classification by categories of belonging and logic. There can be 6 categories: Construction [C], Furniture [F], Decor [D], Light [L], Technology [T], System [S]. Each object must be named in accordance with the following layout:[Categories] [Object Name] [Sub Object Name] [Sub Object ID]
Example:
F Kitchen Door 001
T TV Button 004
L Lamp Bulb 001
All this may sound strange, but such a classification helps to not get lost in large projects and can instantly catch the problem (for example, through messages from the console rendering).
Given this, call our leg as “F Chair Leg 001” and set the grid is black:
The last thing we need to do – to increase the radius of the legs. Yes, check out our radius now. You’ll be surprised, but the range decreased. This is not surprising – the radius has decreased from over turbosmooth. Correct radius is very simple – select all the edges, turn the Scale (hotkey R), turn the percent snap toggle, and scale edges by X and Y on 110%. That’s it.
Now, working with the back foot. As a basis we take the front foot.
Move the top vertex of leg so that the top was at 950 mm.
Select large vertical edge and use Connect with two segments. Move new edge to 50 mm. Result:
We place our legs on their place, create copy-instances of these, and place them too.
Now, we make the wooden walls that hold the chairs.
This object is made in the form of a letter X.
Draw a line, half our letters X, with coordinates:
215,051 mm, 253,033 mm, 0mm
0mm, 0mm, 0mm
215,051 mm, -253,033 mm, 0mm
Use the line opportunity to be a 3D – in Edit Rendering rollout, turn on the check Enable in Renderer and Enable in Viewport. In the group Renderer, select the item Rectangular, set the value of Length = 34 mm, Width = 26 mm. We move our object to a height of 440 mm:
Convert to Edit Poly, remove the excess edge at the front polygon.
Select the next edge, and apply the Connect with the parameters 2, 80, 0:
Select the next edge, and apply the Connect with the parameters 2, 85, 0:
Select the next edge, and apply the Connect with the parameters 2, 98, 0:
Select the object sub level (hotkey 5), and use Slice Plain where X = 0.
Move Slice Plain at -2mm on X and use it again.
We remove all that is greater than 0 on X:
Apply the modifier Mirror. Move Mirror Center on X to 0, and enabled the check Copy:
Use Turbosmooth with 3 iteration.
Apply for all legs modifier Normal.
As a result, we have the following structure:
Now, let’s do chair back
Create a box with the following dimensions (Create in Front View):
Length: 220 mm, Width: 250 mm, Height: 10mm.
Put it on 125,0 mm in X, 258,098 mm in Y, 815,0 mm in Z.
Convert it to Edit Poly.
Select the vertex with the lower right side and move them toward the rear legs.
Select the next edge, and apply the Connect with the parameters 2, 97, 0:
Select the next edge, and apply the Connect with the parameters 1, 0, -98:
Remove those polygons:
Apply the modifier Mirror. Move Mirror Center on X to 0, and enabled the check Copy.
Convert the resulting object in Edit Poly. Select the vertices that are in the 0 to X. Apply function Weld Vertexes, with parameter 0,1 mm:
Move top center vertexes to 10 mm in Z.
Select the following vertices and move them to 5 mm in Y:
Use Turbosmooth with 3 iteration.
It now remains only to make a hole in the back of the chair. Someone may say that it is very simple, by Boolean operands. But NEVER do it.
Standard, paragraph 8: Never use Boolean!
This rule is related to the fact that Boolean completely kills topology.
Example of killed topology:
Let’s do right hole. To do this, make cylinders. The first cylinder should be at the following coordinates: X = 0 mm, Y = 770,448 mm, and pass through the back of chair. Making his radius of 18 mm. Set him 8 segments and disable the Smooth. Making an array of three such cylinders, by Z = 48 mm:
Disable TurboSmooth, take front view, and use Connect to add the additional lines.
Select the next edge, and apply the Connect with the parameters -2, -85, -1200:
Now, use the Cut tool, to add the edge on the path of our cylinders (in the form of Front and in the form of Back). Remove the extra edge:
Remove the central polygons. Weld central vertex.
Select our central edge, and apply Chamfer with parameters 1,00 mm.
As a result, we obtain the template for the back.
Select the appropriate ring (Use Border sub level) and apply Bridge with parameters 1, 0, 0:
Select the obtained edges and use Connect with parameters 2, 65, 0:
Repeat this procedure with all of our holes:
Add a some additional edges, that model looked clean and tidy (I will not describe this process because it is long and not interesting):
Turn on Turbo Smooth:
Unhide All, and look at the result:
Obviously, you need to raise the back slightly upper. Raises her at 10mm on Z and let’s proceed to the seat. We will simulate the structure by texture, that’s why we need a relatively simple seat.
Create a Box, at the height of 457,0 mm and the contour of area chair:
Now we will create an additional segment and move the edge that’s seat does not intercept with the base. I also made a gap in 2mm, for the nice reality:
Select the next edge, and use Connect with parameters 2, 60, 0:
Select the next edge, and use Connect with parameters 2, 60, 0:
Select the next edge, and use Connect with parameters 2, 80, 0:
Move to the upper section to -10 mm in Z:
Remove the central vertex, which is 0 on X.
Apply the modifier Mirror. Move Mirror Center on X to 0, and enabled the check Copy.
Remove the excess, the central edge on Y.
Use Turbosmooth with 3 iteration:
PART 03: FINISH
So, we have a complete model, fully compliant with our standards.
Turbosmooth x3 (Render): 65 816 vertices, 131 072 range.
Without Turbosmooth (viewport): 1076 vertices, 1014 polygons.
Scene weighs: 384KB.
You can download the complete scene here.
In the following tutorials we will learn how to correctly apply the materials and do render in Mental Ray / IRay.
Tutorial by Gates Bengamin 2011


























































Clean and clear tutorial..it’s a great work man!
realy cool
I am happy with your 3d tutorial’s very nicely presented…good luck
so nice dear
awesome sharing
Hi,can you explain “Select large vertical edge” in “Select large vertical edge and use Connect with two segments. Move new edge to 50 mm. Result” : I’m stuck there and I don’t understand what to do… Thanks !
Its very nice…thank you
I know the theme of this wordpress, is sourceopen? or sourceforge? from elegantthemes… However the tutorial is nice thanks for sharing
niceeeeee!!, thanks for sharing
really nice
this is really AWESOME!!