“Cheese Platter ” by Hau Ming (Jamie) Li
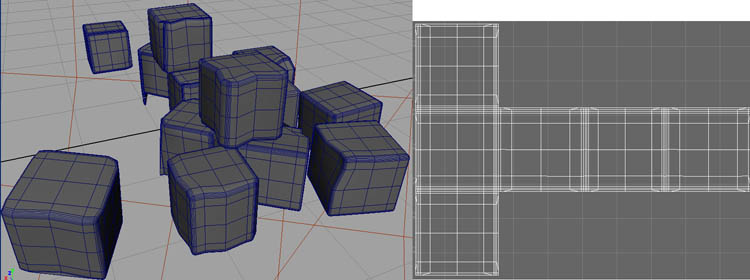
For the cheese cubes, I basically modeled one good one in Polygon with rounded edges, and UV mapped it . Then I duplicated and shaped them with a lattice individually to make them look less uniform and less perfect. Then when I placed them, I rotate each cube so the camera can see one side of the textures. This will save you time instead of modeling, uv mapping and texturing them individually.
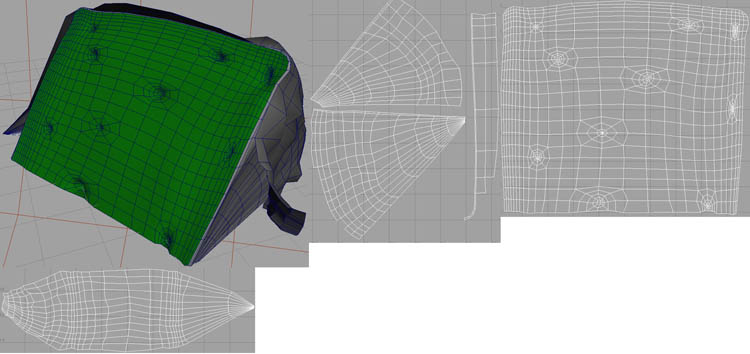
For the blue cheese, I used a Polygon cube, shaped it, and then extracted the Polygons to separate the skin and the cheese. I duplicated the skin to make the wrapper. I deleted the Polygons at the back of the cheese skin because you are not going to see it. I used a lattice to bend and shape the wrapper.
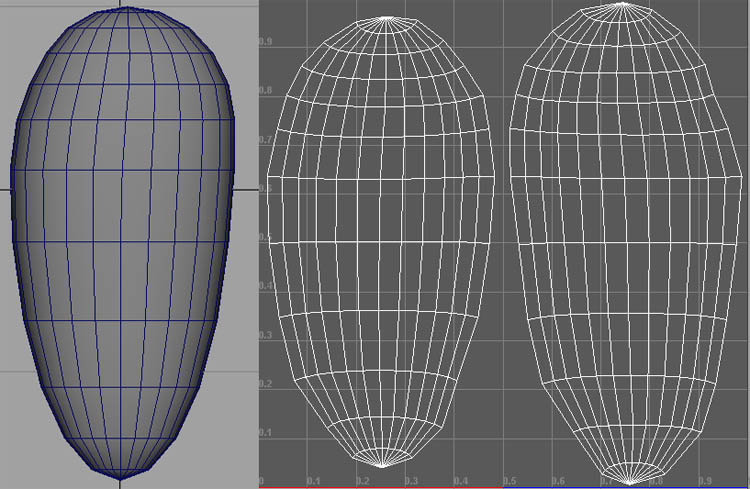
For the almonds, I used a NURBS sphere, converted it to polygons , reversed normals , and UV mapped it.
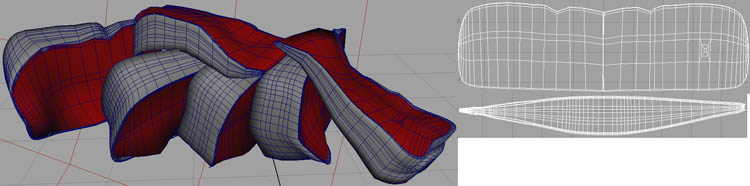
For the Brie cheese, I used NURBS CV curves, which I lofted, and then shaped them by pulling the vertices. I converted the surfaces to Polygons and UV mapped them.
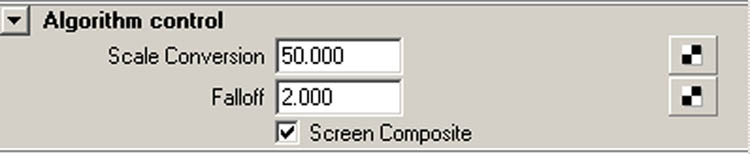
Subsurface Scattering:
For an organic character, the conversion scale will generally remain small. However, the fruits and cheese have translucencies which are a lot higher. Therefore, there will be more noise to balance out, which means higher values for the scale conversion.
However, there is more than one way to balance the noise without having such insane numbers for the scale conversion. You can play with the numbers of the samples of the lightmap in addition to the minimal numbers of the scale conversion.







Latest Comments